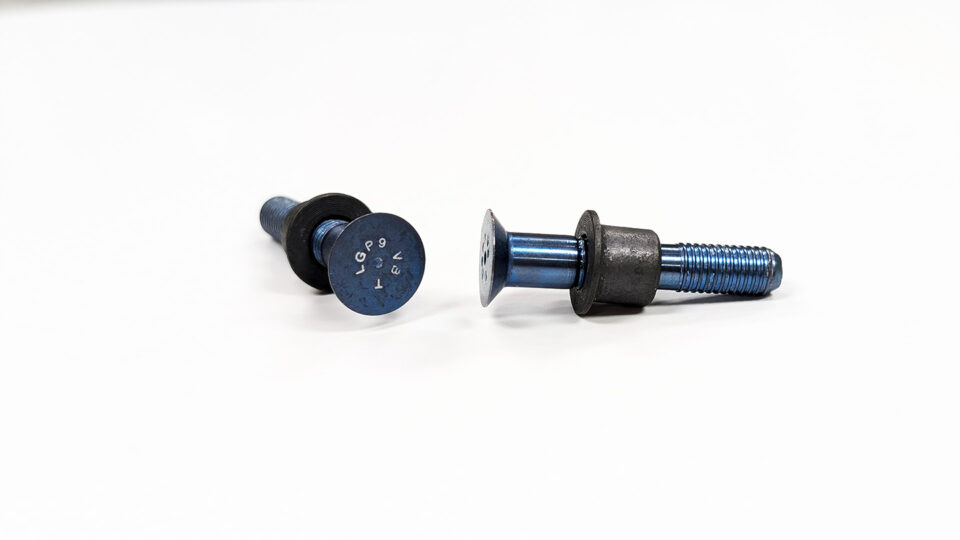
Among the myriad fastening solutions employed in aircraft construction, one stands out for its versatility, strength, and efficiency: the HI-LOK™. These specialized fasteners have become ubiquitous in aerospace applications, offering unique advantages that make them indispensable in aircraft assembly and maintenance.
HI-LOKs™ are revered for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for securing critical components in aircraft structures. Constructed from high-strength materials such as titanium or stainless steel, HI-LOKs™ provide unparalleled reliability and durability, ensuring the structural integrity of aerospace assemblies under extreme conditions. The HI-LOK™ system’s integrated design features ensure consistent torque and preload values, enhancing the fatigue life of aerospace structures. The HI-LOK™ fastening system comprises two components: a threaded pin and a threaded collar, effectively blending the benefits of a rivet and a bolt-nut system. The system’s automatic breakoff design eliminates the need for torque inspection, streamlining the installation process and improving efficiency. Furthermore, the lightweight HI-LOK™ collar contributes to weight savings without compromising strength, making it an ideal choice for weight-conscious aerospace applications.
Where You’ll Find Them:
HI-LOKs™ can be found anchoring a multitude of components, from wing panels and fuselage sections to interior fixtures and access panels. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in critical areas where safety and performance are paramount, such as wing-to-body junctions, empennage assemblies, and engine nacelles. From commercial airliners to military aircraft, HI-LOKs™ play a vital role in ensuring the structural integrity and aerodynamic efficiency of modern aerospace platforms.
Traditional Removal:
Despite their many advantages, removing HI-LOKs™ using traditional methods presents a significant challenge. Typically, the process involves drilling out the rivet head to release the shank from the material, a labor-intensive and time-consuming task. Moreover, the hardness of the rivet material can make drilling more difficult, increasing the risk of tool wear and breakage. Here are the basic steps to removing HI-LOKs.
Setup: Identify Fastener and Select Proper Tooling
- Identify the Hi-Lok fastener by checking its head style (flush or protruding) and shank diameter. This information helps you select the correct drill bit and tooling.
- Select the correct drill bit: Choose a drill bit slightly smaller than the shank diameter of the Hi-Lok fastener. Typically, a bit about 90% of the shank diameter is used to avoid damaging the surrounding material. Gather the remaining tools, including a drill, center punch, pin punch, hammer, and safety glasses. Ensure the work area is stable, and you have a clear view of the fastener.
- Center Punch the Fastener Head: Use a center punch to make a small indentation in the center of the fastener head to help keep the drill bit centered during drilling. Strike the center punch lightly with a hammer to create a small dimple in the middle of the fastener head.
- Drill into the Fastener Head: Position the drill bit into the center-punched mark and start drilling slowly to maintain control and alignment. Gradually increase the speed, drilling deep enough to remove the fastener head without drilling through the shank entirely. Check frequently to avoid over-drilling and damaging the surrounding structure.
- Remove the Fastener Head: Once drilled deep enough, the fastener head should be weakened. Use a pin punch and hammer to gently tap around the edge, breaking the head free from the shank. If necessary, use a larger punch to knock the head off completely.
- Drive the Pin Out: After removing the head, use a pin punch to drive the remaining shank out from the head side. Tap the punch with a hammer until the shank is completely removed from the hole.
- Clean and Inspect the Hole: Inspect the hole for any remaining debris or fastener material. Optionally, use a deburring tool to smooth out any rough edges left from the drilling process.
A Better Way Forward:
Enter the E-Drill, a cutting-edge solution that has transformed the rivet removal process in the aerospace industry. Powered by electro-discharge machining (EDM) technology, the E-Drill offers rapid, precise, and damage-free removal of solid shank rivets, including HI-LOKs™. Unlike traditional methods that rely on mechanical force and drilling, the E-Drill utilizes electrical discharge to erode the rivet material, leaving behind a clean, precise cut without damaging the surrounding structure.

The introduction of the E-Drill represents a significant advancement in aerospace maintenance technology, offering unparalleled efficiency, precision, and reliability in rivet removal operations. By streamlining the removal process and minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding structures, the E-Drill enables aerospace engineers and maintenance professionals to work more efficiently and effectively, reducing downtime and ensuring the continued safety and reliability of aircraft systems. As the industry continues to evolve, the E-Drill stands as a testament to the power of innovation in driving progress and efficiency in aerospace maintenance operations.
Setup
Select the HI-LOK™ to be removed from the drop-down menu in the fastener library. Ensure the correct electrode is installed, and choose the appropriate locator (e.g., Button Head or Vacuum Flush Head Locator).
If you haven’t programmed the machine to remove HI-LOKs™ yet, use the “Build Fastener” screen to input the necessary data. Gather the relevant properties from the manufacturer’s fastener drawings, which are usually easy to find online. You’ll need information such as head type (flush or protruding), radius, head height, head angle (for flush fasteners), and shank diameter.
Input this data into the Touch Screen Display (TSD), which will recommend the correct electrode and locator tool. Once the fastener is configured, it will be saved in the fastener library for future use. For detailed instructions on how to build a fastener on the E-Drill system, visit this E-Drill Acadcemy Page on identifying and building fasteners.
Step 1: Locate
Position the Button Head Bushing or Flush Head Vacuum locator precisely over the HI-LOK’s™ head. It’s crucial to align the locator concentrically around the fastener to ensure accuracy. Once in position, insert the hand tool and apply gentle pressure, enough to seal the rubber O-Ring around the fastener head.
Step 2: Cut
Activate the E-Drill by squeezing the trigger and hold until the display light indicates the status of the cut. This process will usually take between 7-12 seconds depending on the fasteners shank diameter and material.
Step 3: Punch
The final step involves using a punch that matches the size of the electrode used for the cut. Align the punch with the cut ring of the fastener and apply a moderate force before pulling the trigger. The shank of the fastener will then be severed from the fastener head, leaving a clean and empty hole. The precise and clean cut from the E-Drill usually ensures that the pin can be removed with minimal effort.
Advantages of Using E-Drill for HI-LOK™ Removal:
- Speed: The E-Drill significantly speeds up the removal process compared to traditional drilling methods, saving time and money.
- Safety for Technicians: E-Drill’s method eliminates the need for intense physical handling and exposure to sharp remnants or heavy equipment, making it a safer option for technicians.
- Aircraft Structural Integrity: The precision of the E-Drill minimizes the risk of accidental damage to surrounding structures, preserving the integrity of the aircraft.
- No FOD or Debris: Unlike drilling, the E-Drill does not create metallic shavings or debris, eliminating the risk of foreign object debris (FOD) that could compromise aircraft safety and operation.
By adopting the E-Drill for HI-LOK™ removal, maintenance teams can achieve a more efficient, safer, and cleaner operation, aligning with the best practices in aerospace maintenance.
Here’s a list of HI-LOK™ Part Numbers for use with E-Drill:
HI-LOK™ Pin Part Numbers:
| Part Number | Material | Head Style |
|---|---|---|
| HL10 | Titanium | Protruding Shear |
| HL11 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL12 | Titanium | Protruding Tension |
| HL13 | Titanium | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL18 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Shear |
| HL19 | Alloy Steel | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL20 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Tension |
| HL22 | Aluminum Alloy | Protruding Shear |
| HL23 | Aluminum Alloy | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL30 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL31 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL32 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HL40 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL41 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL48 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HL49 | CRES | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL54 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL58 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL59 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL62 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Shear |
| HL63 | Alloy Steel | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL64 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Tension |
| HL65 | Alloy Steel | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL67 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL110 | Titanium | Protruding Shear |
| HL111 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL112 | Titanium | Protruding Tension |
| HL113 | Titanium | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL136 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HL140 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL144 | CRES | Others |
| HL220 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Tension |
| HL227 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL240 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL241 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL248 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HL326 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Tension |
| HL349 | Titanium | 130° Flush Crown Shear |
| HL358 | Titanium | Protruding Shear |
| HL318 | Alloy Steel | Protruding Shear |
| HL410 | Titanium | Protruding Shear |
| HL411 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL412 | Titanium | Protruding Tension |
| HL413 | Titanium | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL440 | CRES | Protruding Shear |
| HL441 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL443 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL448 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HL454 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HL523 | Titanium | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL633 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL701 | Nickel Based Alloy | 100° Flush Shear |
| HL730 | Nickel Based Alloy | Protruding Tension |
| HL731 | Nickel Based Alloy | 100° Flush Tension |
| HL754 | Nickel Based Alloy | Protruding Shear |
| HLM10 | Titanium | Protruding Shear |
| HLM11 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HLM12 | Titanium | Protruding Tension |
| HLM32 | Nicked Based Alloy | Protruding Tension |
| HLM36 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HLM41 | CRES | 100° Flush Shear |
| HLM211 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HLM213 | Titanium | 100° Flush Tension |
| HLM310 | Titanium | Protruding Shear |
| HLM312 | Titanium | Protruding Tension |
| HLM336 | CRES | Protruding Tension |
| HLM611 | Titanium | 100° Flush Shear |
| HLM612 | Titanium | Protruding Tension |
HI-LOK™ Collar Part Numbers:
| Part Number | Material | Pin Shank Diameter |
|---|---|---|
| HL1087 | CRES | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL1094 | CRES | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL175 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL185 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL198 | Titanium | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL273 | CRES | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL278 | CRES | 1/64 Oversize |
| HL289 | CRES | 1/32 Oversize |
| HL373 | CRES | 1/32 Oversize |
| HL374 | Aluminum | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL375 | CRES | 1/32 Oversize |
| HL379 | Titanium | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL478 | CRES | 1/32 Oversize |
| HL70 | Aluminum | Nominal |
| HL73 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL75 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL77 | Aluminum | Nominal |
| HL78 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL79 | Aluminum | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL82 | Aluminum | Nominal |
| HL84 | Aluminum | 1/32 Oversize |
| HL86 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL87 | CRES | 1/64 Oversize |
| HL89 | CRES | Nominal |
| HL93 | CRES | 1/32 Oversize |
| HL94 | CRES | Nominal,1/64 Oversize |
| HL97 | CRES | Nominal |
Other HI-LOK™ Part Numbers
| Part Number |
| HL412VAP10-5 |
| HL19PB70-8-5 |
| HL2075-6AW6 |
| HL221-8-7 |
| HL412VAP10-4 |
| HL2075-6AW6 |
| HL412VAP10-4 |
| HL412VAP10-5 |
| HL412VAP10-4 |
| HL221PN6-8 |
| HL48-8-10 |
| HL2075-6AW8 |
| HL2075-6AW7 |
| HLM10-05-03 |
| HL11VAZ5-6 |
| HL18PB-6-16 |
| HL413VAP10-4 |
| HL2075-6AW6 |
| HL19PB70-8-5 |
| HL18PB70-6-8 |
| HL221-8-6 |
| HL412VAP10-5 |
| HL413VAP10-4 |
| HLT423AP14-21 |
| HL412VAP10-4 |
| HL2075-6AW6 |
| HL2075-6AW7 |
| HL2075-6AW8 |
| HL2075-6AW6 |
| HL2075-6AW6 |
| HL221-6-6 |
| HL221PN6-8 |
| HLM10-05-03 |
| HL22077-5-3 |
| HL48-8-25 |
| HL2075-6AW7 |
| HL2075-6AW8 |
| HL413VAP10-4 |
| 145-174-9105 |
| HL40-6-5 |
| HL221PN6-8DS |
| HL412VAP10-5 |
| HL413VAP10-4 |
| HL412VAP10-4 |
| HL412VAP10-5 |
| HL11VAZ5-5 |
| HL18PB6-16 |
| HL40-8-18 |
| HL413VAP10-4 |
HI-LOK, HI-LITE, HI-TIGUE, HL, HST, HLT, HSTR and HLR are trademarks of HI-SHEAR Corporation, subsidiary of LISI AEROSPACE. Perfect Point EDM, Corp. has no affiliation with Hi-SHEAR or LISI AEROSPACE or any of LISI AEROSPACE’s subsidiaries.